
What Does the Mitochondria Do? 10 Ways to Boost Mitochondrial Health for Energy, Brain Health and Vitality
June 4, 202510 Natural Ways to Increase GLP-1 Hormone for Blood Sugar Balance and Weight Loss

Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) is a hormone secreted mainly by the digestive system in response to food. It slows down the stomach's emptying and promotes a feeling of satiety. In addition to this, GLP-1 also increases insulin production and decreases glucagon production.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that triggers cells to take in sugar (glucose) from the blood, thus lowering blood sugar. Glucagon triggers the release of glucose into the bloodstream, increasing blood sugar.
What is GLP-1?
By helping to increase satiety, slow down digestion and stabilize glucose levels, GLP-1 is an important hormone for those with diabetes, obesity or any other metabolic issues. For this reason, medications that mimic GLP-1 have quickly become the most popular drugs on the market today.
What are GLP-1 Analogs?
GLP-1 analogs are medications that bind to GLP-1 receptors, thus mimicking the same effects of the hormone. Due to its ability to balance blood sugar and control appetite, analog medications have been approved to treat both type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Some of the GLP-analog drugs available in Canada include Tirzepatide, available as “Mounjaro,” or Semaglutide, available as “Ozempic.” Both are administered as a weekly injection.
If you believe you are a candidate for a GLP-1 analog drug, you can speak to your doctor.
However, for the rest of us, we can encourage our own body to increase GLP-1 production to reduce cravings, stabilize blood sugar and increase energy levels.
10 Ways to Increase GLP-1 Production
1. Protein
Protein is the most satiating macronutrient. Therefore, consuming adequate protein with each meal will keep you feeling full longer. Our body also needs protein to make the GLP-1 hormone, as GLP-1 is made from amino acids, the building blocks of protein. In particular, amino acids such as tryptophan, phenylalanine, valine and glutamine help to stimulate GLP-1 production. Here are some foods rich in these amino acids:
- Glutamine: Beef, chicken, eggs, red cabbage
- Tryptophan: Chicken, Turkey, Pumpkin Seeds, Salmon.
- Phenylalanine: Eggs, pumpkin seeds, hemp seeds, sunflower seeds
- Valine: Chicken, beef, tuna, pumpkin seeds, navy beans
2. Soluble Fibre-Rich Foods

GLP-1 is produced in the gut. Our gut is also home to trillions of microbes, which are essential to our health. Gut microbes need to eat too! They love to eat soluble fiber. When they are well-fed, they produce short-chain fatty acids such as butyrate, propionate and acetate. These short-chain fatty acids then bind to L-receptors and produce GLP-1. Basically, if your microbiome is well-fed and happy, you will also feel well-fed and happy! Here are some foods rich in soluble fiber
- Artichoke
- Asparagus
- Chicory
- Black beans, Kidney beans and lima beans
- Brussels Sprouts
- Broccoli
- Sunflower Seeds
- Turnips
3. Calcium-rich Foods
A 2013 study demonstrated that calcium consumption led to a 22% increase in GLP-1 production. In this double-blind crossover study, 10 healthy males consumed two nutritionally identical meals, differing only in calcium content. With higher calcium intake, not only were GLP-1 levels elevated, but insulin levels also increased, and a suppression of appetite was observed.
Here are some calcium-rich foods:
- Dairy
- Kale
- Broccoli
- Sardines
- Sesame seeds
- Almonds
4. Avocado
We probably don’t need a scientific study to tell us that an avocado is quite filling, but there is one, nonetheless. A 2019 study demonstrated that replacing the carbohydrate source in a meal with a half or whole avocado increased the satiety hormones, such as GLP-1, leptin, and CCK (cholecystokinin). Also, the subjects were more satisfied with the meal. This is, of course, due to the mono-unsaturated fat and fiber content in the avocado.
5. Olive Oil
Similarly to avocado, olive oil has been shown to increase GLP-1 due to its mono-unsaturated fat content. A 2021 research review cited several studies which have demonstrated this. Mono-unsaturated fats in general have been shown to increase GLP-1 production more so than saturated fats.
6. Omega-3 Fatty Acid-Rich Foods
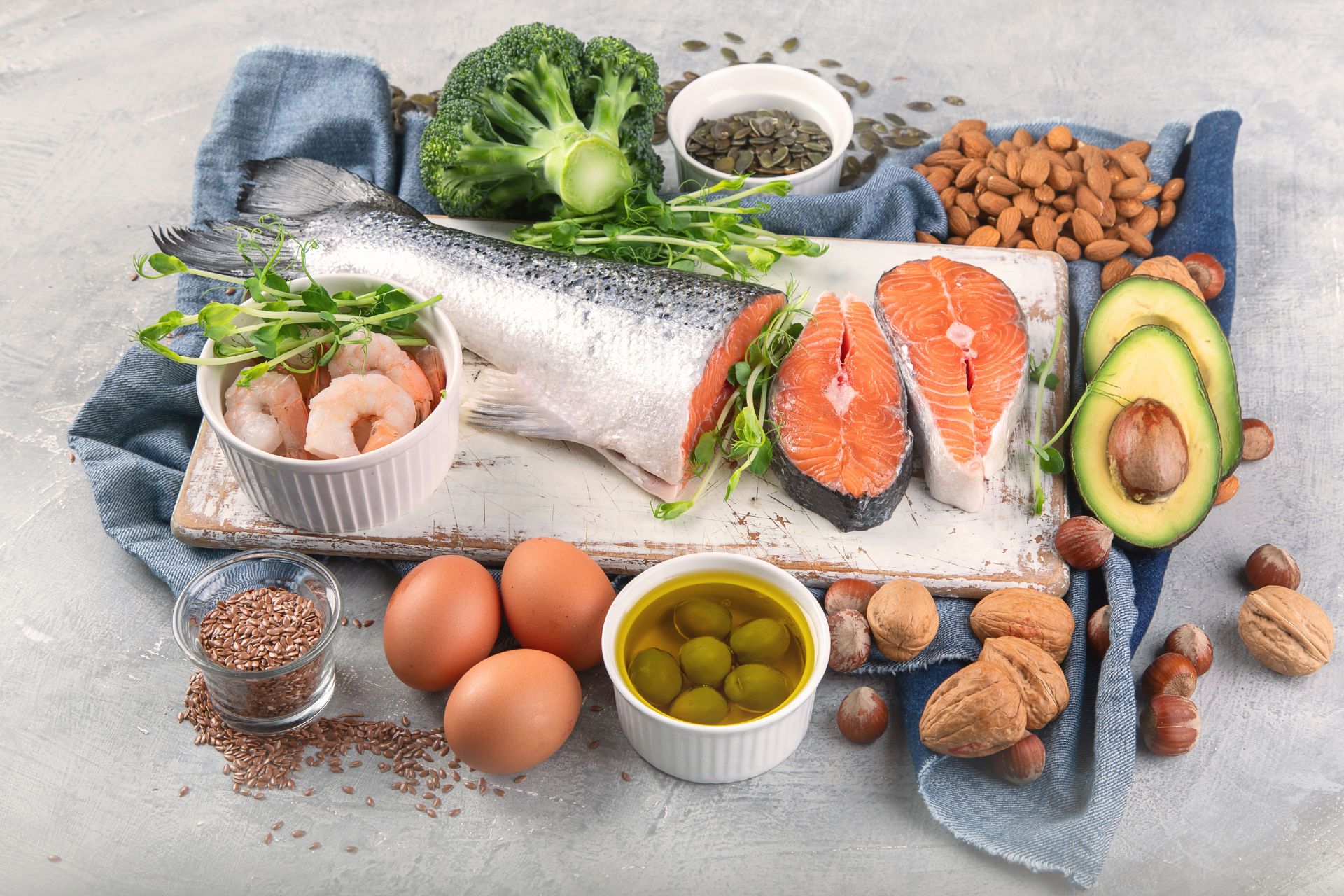

In addition to consuming mono-unsaturated fats from avocados, avocado oil, and olive oil, long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, such as the ones found in fish, are also important for satiety and GLP-1 production.
It is easy to remember the fish that are high in omega-3 fatty acids by the acronym SMASH – sardines, mackerel, anchovies, salmon and herring. You may even say these fish will “smash” your hunger.
If you don’t like fish or you find it difficult to incorporate these foods in your diet consistently, then you can also take a fish oil supplement.
7. Yerba Maté Tea
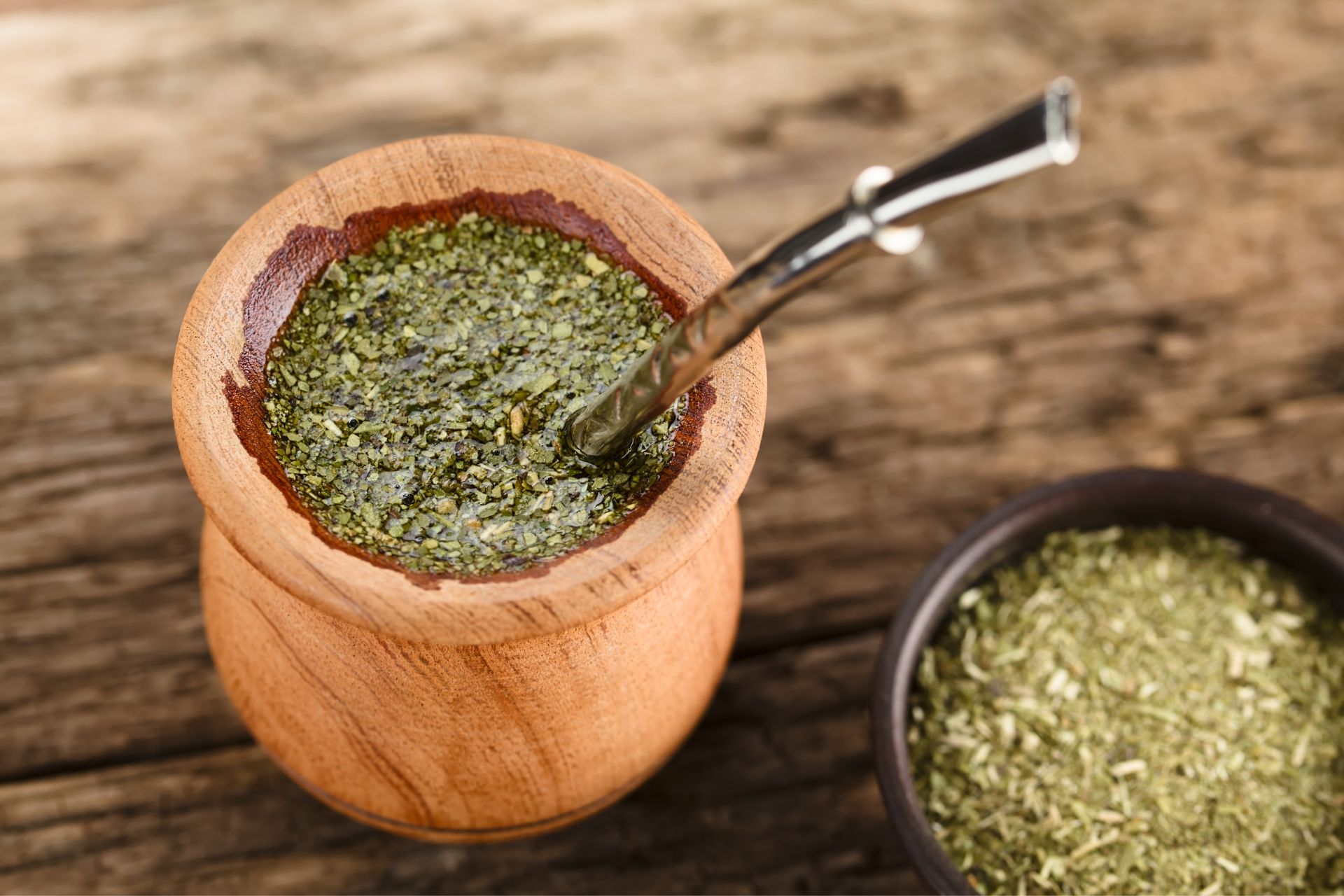

A traditional South American tea made from the Ilex Paraguariensis plant. This tea has been shown in studies to increase GLP-1 levels. However, this tea also contains caffeine, so if you are going to consume it, make sure it is a morning beverage, so it does not interfere with sleep.
8. Berberine

Berberine is an active compound found in different plants such as Oregon grape, barberry and goldenseal.
Berberine in supplement form has grown in popularity due to its potential benefits for cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Studies have shown that not only can it stimulate GLP-1 secretion, it can also reduce the oxidative stress of mitochondria. Please see our previous blog for more information on the mitochondria.
9. Red Ginseng
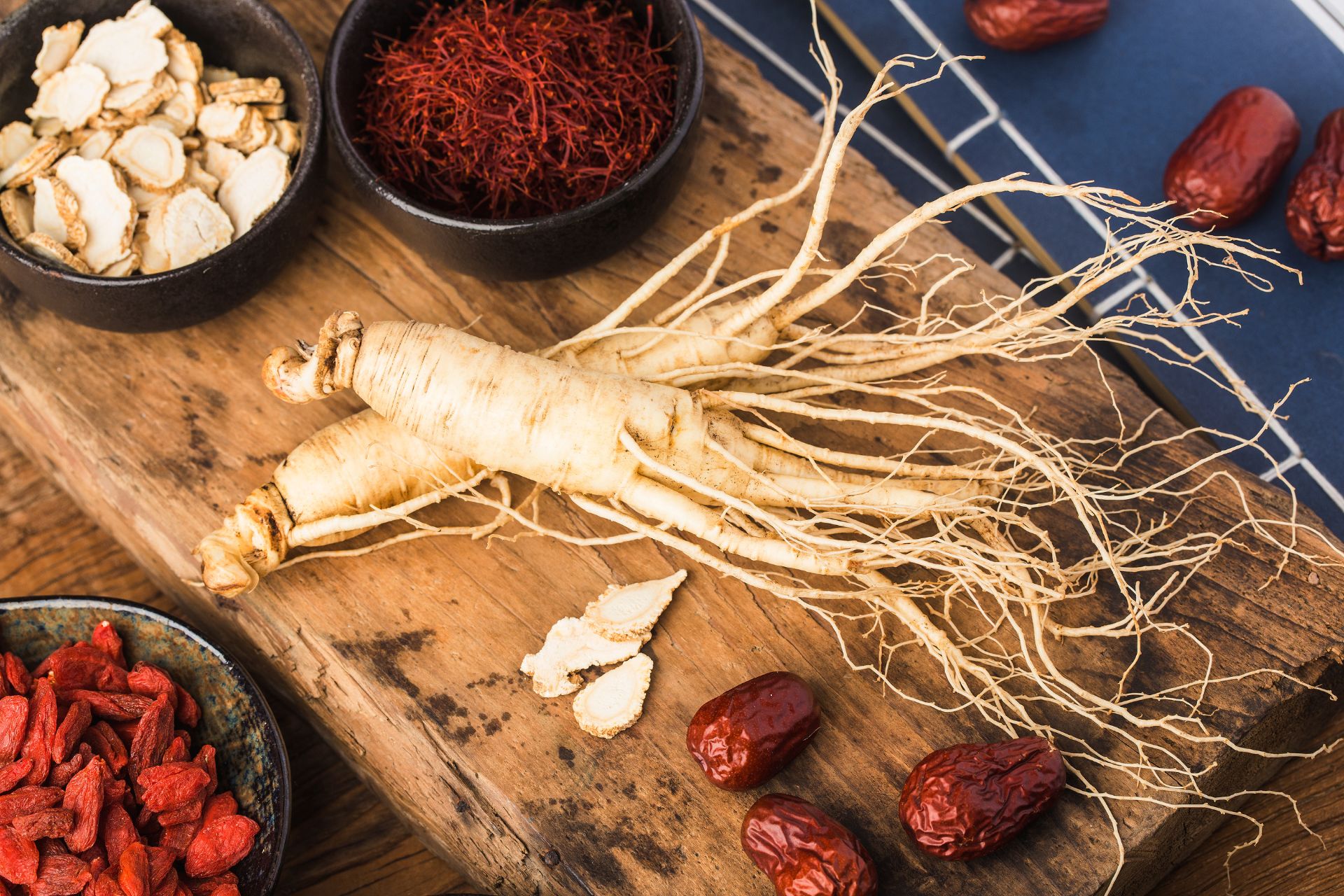

Red ginseng, or Panax ginseng, is traditionally used to increase energy levels. It has also been shown to have an anti-diabetic effect, although the particular mechanism was not always entirely understood.
However, studies have now shown that the ginsenosides in panax ginseng can increase GLP-1 production. Panax ginseng can be consumed in tea, tincture or capsule.
While it does not contain any caffeine, it is considered to be a very stimulating herb; therefore, it is recommended to be taken earlier in the day.
10. Turmeric

Is there anything turmeric isn’t good for? Curcumin, the active compound in the spice turmeric, has been shown to increase GLP-1 production.
Turmeric can be consumed as a whole food, in cooking, teas or by blending or juicing the fresh rhizome. However, turmeric can also be taken as a supplement, either as turmeric or curcumin extract. Black pepper or piperine has also been shown to increase the bioavailability of curcumin.
Putting it all Together (On Your Plate)
So, how do you build a GLP-1 producing meal?
Well, let’s start with the building blocks of the hormone itself. We need amino acids. This means protein. You could enjoy some chicken, beef or omega-3 rich fish, perhaps you have seasoned it with spices such as turmeric and black pepper.
Remember, there are plant sources of protein too, such as beans, nuts and seeds. Many of these plant-based foods are also good sources of fiber. Once you have your protein sources, you can add in the vegetables. Perhaps some fiber-full, calcium-rich vegetables, such as kale or broccoli.
Then you’re going to drizzle some good quality olive oil over the veggies, maybe even adding an avocado on the side.
Add more seasoning, sprinkle good quality sea salt, maybe a squeeze of lemon, and you have a nutrient-dense, highly satiating and satisfying meal.
If you’re getting hungry now, it may be time to eat; just don’t forget to feed your microbiome too!
*****************
Kirsten Colella, CNP, is a Holistic Nutritionist, graduating from the Institute of Holistic Nutrition with high honours; Kirsten is also a certified yoga teacher. As a yogi who teaches individuals, groups and soon online, Kirsten does her best to live a full yoga-styled life, incorporating the best from herbs with her farm-fresh foods. Living on a farm with her family, Kirsten loves to prepare a wide variety of farm-to-table meals, sharing her delicious recipes, colourful food pics and health-promoting food ideas on our Instagram page @essentialbalanceholistic.
*****************



